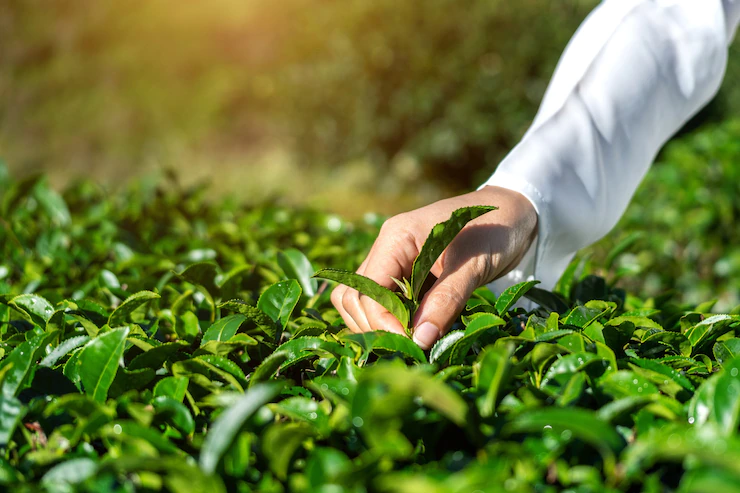
Technology is used in agricultural genomics to examine and categorize plant DNA to create new, specialized crop varieties.
These novel crops can potentially increase the productivity and sustainability of numerous plant and livestock species and contribute to solving various global food issues.
It’s critical now more than ever to hasten the creation of novel crops that yield more, are heat or drought-resistant, and require fewer pesticides due to the growing global population, changing climate, and mounting environmental challenges. Genomic advancements could speed up the creation of crops with good agronomic features.
The selection of features advantageous to agriculture is just one example of how genomic breakthroughs have advanced crop growth. Higher agricultural yields, stress tolerance, and pest resistance are typical examples of these promising features. Genomics can hasten the evolution of plants and animals with features that improve sustainability or satisfy consumer demand.
The core principle behind agrigenomics
Agronomists, breeders, and gardeners have employed traditional plant breeding techniques to increase the production of plants for hundreds of years. Currently, cutting-edge genomic methodologies and techniques offer instruments to battle breeding initiatives like boosting crop production and stress tolerance that had previously gone unanswered.
Additionally, farmers worldwide utilize agrigenomics to speed up and enhance plant and animal breeding techniques for raising cattle and other food products. By studying these plants, farmers and scientists can learn more about the genes that affect growth rate, seed and fruit qualities, and vulnerability to infectious diseases and climate change.
Agrigenomics, or agricultural genomics (the use of genomics in agriculture), has increased sustainable production and offered solutions to the world’s expanding food issues, and it will continue to do so. With contemporary technologies, farmers, breeders, and researchers can swiftly identify genetic markers linked to desirable features, guiding cultivation and breeding decisions.
In addition, farmers worldwide, particularly in industrialized nations, are implementing agrigenomics to improve and hasten the processes of plant and animal breeding. By investigating these plants, farmers and researchers can gain more knowledge about the genes that affect growth rate, the characteristics of the seeds and fruits, and sensitivity to climatic change and disease agents.
The importance of agrigenomics
- Agrigenomics helps to develop crops that are better and more resistant to pests, diseases, drought, cold, floods, and other factors that affect their growth.
- It helps to create more nutrient-dense foods and to grow enormous quantities of food in a small space.
- It also helps to create a robust herd of disease-resistant, high-quality cattle. The exact prediction of genetic merit, the fine-tuning of selective breeding, the augmentation of desired traits, and the improvement of animal welfare are all made possible with genomics.
- Genomic research benefits aquaculture since it enables aquatic animals to develop more quickly, have better disease resistance, and have higher stress tolerance. Aquaculture feeds the world’s population, which provides vital, high-quality protein.
Conclusion
Crop enhancement can benefit future generations and effectively supply a population that is expanding with food. Genomics maximizes the usefulness, diversity, and yield of resources to contribute to long-term food security.
Additionals: